Why is Breakfast Important?
Breakfast, typically considered the first meal of the day, is derived from “breaking the fast” after a night’s sleep, and is widely considered the most important meal of the day. Far from being a routine, a nutritious morning meal provides essential fuel and nutrients required to energize the body throughout the morning, and support long-term health. Integrating breakfast into your daily routine offers significant physiological and psychological benefits that extend past the morning.
Fueling the Body and Mind.
After an overnight period without food, the body’s glucose (blood sugar) levels are low. Glucose is the primary fuel source for the body, particularly the brain and muscles. Breakfast replenishes these stores, effectively “jump-starting” the metabolism and providing the sustained energy needed for physical activity and mental alertness.
- Improved Physical Performance: A balanced breakfast ensures energy availability for daily tasks and physical exertion, preventing the mid-morning fatigue and lethargy that happen when this meal is skipped.
Supporting Weight Management and Appetite Control.
- Appetite Regulation: A breakfast rich in protein and fiber promotes satiety, leading to reduced hunger and a lower likelihood of impulsive snacking on high-calorie, low-nutrient foods later in the day.
- Metabolic Regulation: Eating early in the day signals to the body that ample energy is available, preventing it from entering a “conservation mode” that can slow down the metabolism.
Making a Nutritious Breakfast.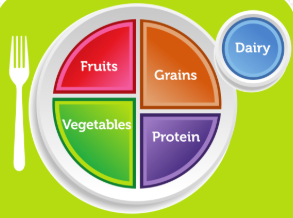
- Whole Grains: Oatmeal, whole-wheat bread, cereal, or bagels.
- Protein: Eggs, Greek yogurt, or nuts.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, bananas, or spinach.
- Dairy: Milk, yogurt, cheese, cottage cheese.









